Cosmetic Facial Injections
Dermal Fillers
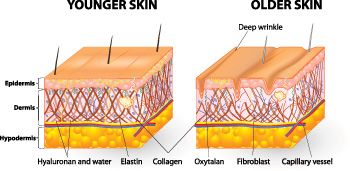
Many methods and substances have been used to treat facial wrinkles and to conceal the effects of aging on the face. In addition to formal surgical procedures, laser treatment and botulinum toxin there are a large number of fillers available which can be injected.
Types: Dermal fillers may be biocompatible or synthetic and are marketed alone or in combination.
Biocompatible fillers have a perceived safety record and are resorbable. However the period of benefit is of limited duration normally lasting about 6 months. Synthetic fillers are permanent but are associated with rejection, migration and granuloma formation and are unable to change with the ageing face. In the case of an adverse reaction removal is almost impossible to achieve. There are few indications in current practice for the injection of synthetic fillers to the correct lines and effects of ageing. They are included for reference rather than recommendation.
Biocompatible Fillers
 Ideally the effects of a filler should last about 12 months. This allows reasonable respite from the injections and also enables accommodation of changes in the face which may occur with continued ageing.
Ideally the effects of a filler should last about 12 months. This allows reasonable respite from the injections and also enables accommodation of changes in the face which may occur with continued ageing.
Collagen
Collagen implants are prepared from three sources: bovine, human or autologous. Collagen synthesis may also be increased by fibroblast stimulation or injection of cultured cells.
Bovine Preparations - This comes in a highly purified or monomolecular form in different concentrations and mixed with local anaesthetic. A test dose is required as approximately 3% of patients demonstrate sensitivity and another 1% will develop sensitivity with treatment. In most patients it will be completely resorbed within 3 to 6 months.
Human Preparations - These are a preparation of human collagen, elastic fibres and other dermal components from screened donors. No pre-treatment skin testing is necessary and the effects last from 3 to 12 months.
Autologous Preparations - These require skin harvest, which is processed into a collagen suspension for injection and requires 2-3 treatments over a 3 month period. This is reported to provide greater than 75% correction for more than a year.
 Injectable Fibroblasts can be cultured from a small skin biopsy and following a test dose at one month a series of 3 injections is given at 2 week intervals. Gradual improvement occurs over 6 months and repeat injections can be prepared as required from the original biopsy.
Injectable Fibroblasts can be cultured from a small skin biopsy and following a test dose at one month a series of 3 injections is given at 2 week intervals. Gradual improvement occurs over 6 months and repeat injections can be prepared as required from the original biopsy.
Polylatic acid stimulates fibroblast production. The effect takes 4 to 6 weeks to achieve but can last for years. This should not be injected superficially as obvious fibrous nodules can result which may be difficult to treat.
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid preparations (hyaluronan) are obtained by bacterial synthesis or from an avian source and are cross linked to varying degrees to maximise viscoelasticity and persistence. Commonly used brands include Restylane and Juvederm. They last between 6 and 9 months and although well tolerated there is a 1% incidence of adverse reactions including granulomatous inflammation and sterile abscesses.
Synthetic Permanent Dermal Fillers
Types Available
Methylmethacrylate has been used for many years as bone cement for joint replacement surgery. However in the skin redness, inflammation and infection may occur. One preparation utilises Methylmethacrylate microspheres suspended in bovine collagen whilst an alternative suspends them in Hyaluronic acid. These are intended to permit even distribution of the microspheres prior to absorption of the collagen or Hyaluronic acid. A series of injections are required to achieve the final result and allergic reactions to collagen may occur.
Polyacrylamide Gel is used alone or in combination with polyvinyl microspheres. The injected volume is reported to diminish by one third post injection and then build up again over the next 2 months. The augmentation is supposed to be permanent but additional injections may be required. This augmentation tends to stay soft but Polyacrylamide gel can act as a reservoir for bacteria and has been associated with a significant delayed infection rate.
Downloads